Kmeans算是是聚类中的经典算法,过程如下:
选择K个点作为初始质心
repeat
将每个点指派到最近的质心,形成K个簇
重新计算每个簇的质心
until 簇不发生变化或达到最大迭代次数
算法中的K需要人为的指定。确定K的做法有很多,比如多次进行试探,计算误差,得出最好的K。这样需要比较长的时间。我们可以根据Canopy算法来粗略确定K值(可以认为相等)。看一下Canopy算法的过程:
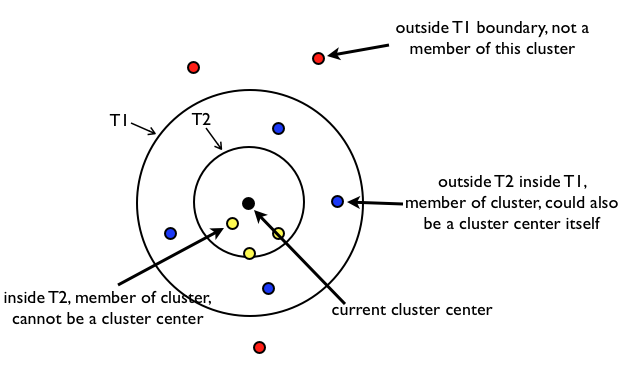
(1)设样本集合为S,确定两个阈值t1和t2,且t1>t2。
(2)任取一个样本点p,作为一个Canopy,记为C,从S中移除p。
(3)计算S中所有点到p的距离dist
(4)若dist<t1,则将相应点归到C,作为弱关联。
(5)若dist<t2,则将相应点移出S,作为强关联。
(6)重复(2)~(5),直至S为空。
Canopy 个数完全可以作为这个K值,一定程度上减少了选择K的盲目性。下面通过Canopy算法对一些点进行计算Canopy的个数,如果仅仅计算K值,则T1没有任何作用,只用指定T2即可,这里使用所有点的平均距离的一半来作为T2.
package cn.edu.ustc.dm.cluster;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import cn.edu.ustc.dm.bean.Point;
/**
* Canopy算法 借助canopy算法计算对应的Kmeans中的K值大小
* 其中对于计算K值来说,canopy算法中的T1没有意义,只用设定T2(T1>T2) 我们这里将T2设置为平均距离
*
* @author YD
*/
public class Canopy {
private List points = new ArrayList(); // 进行聚类的点
private List<List> clusters = new ArrayList<List>(); // 存储簇
private double T2 = -1; // 阈值
public Canopy(List points) {
for (Point point : points)
// 进行深拷贝
this.points.add(point);
}
/**
* 进行聚类,按照Canopy算法进行计算,将所有点进行聚类
*/
public void cluster() {
T2 = getAverageDistance(points);
while (points.size() != 0) {
List cluster = new ArrayList();
Point basePoint = points.get(0); // 基准点
cluster.add(basePoint);
points.remove(0);
int index = 0;
while (index < points.size()) {
Point anotherPoint = points.get(index);
double distance = Math.sqrt((basePoint.x - anotherPoint.x)
* (basePoint.x - anotherPoint.x)
+ (basePoint.y - anotherPoint.y)
* (basePoint.y - anotherPoint.y));
if (distance <= T2) {
cluster.add(anotherPoint);
points.remove(index);
} else {
index++;
}
}
clusters.add(cluster);
}
}
/**
* 得到Cluster的数目
*
* @return 数目
*/
public int getClusterNumber() {
return clusters.size();
}
/**
* 获取Cluster对应的中心点(各点相加求平均)
*
* @return
*/
public List getClusterCenterPoints() {
List centerPoints = new ArrayList();
for (List cluster : clusters) {
centerPoints.add(getCenterPoint(cluster));
}
return centerPoints;
}
/**
* 得到的中心点(各点相加求平均)
*
* @return 返回中心点
*/
private double getAverageDistance(List points) {
double sum = 0;
int pointSize = points.size();
for (int i = 0; i < pointSize; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < pointSize; j++) {
if (i == j)
continue;
Point pointA = points.get(i);
Point pointB = points.get(j);
sum += Math.sqrt((pointA.x - pointB.x) * (pointA.x - pointB.x)
+ (pointA.y - pointB.y) * (pointA.y - pointB.y));
}
}
int distanceNumber = pointSize * (pointSize + 1) / 2;
double T2 = sum / distanceNumber / 2; // 平均距离的一半
return T2;
}
/**
* 得到的中心点(各点相加求平均)
*
* @return 返回中心点
*/
private Point getCenterPoint(List points) {
double sumX = 0;
double sumY = 0;
for (Point point : points) {
sumX += point.x;
sumY += point.y;
}
int clusterSize = points.size();
Point centerPoint = new Point(sumX / clusterSize, sumY / clusterSize);
return centerPoint;
}
/**
* 获取阈值T2
*
* @return 阈值T2
*/
public double getThreshold() {
return T2;
}
/**
* 测试9个点,进行操作
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
List points = new ArrayList();
points.add(new Point(0, 0));
points.add(new Point(0, 1));
points.add(new Point(1, 0));
points.add(new Point(5, 5));
points.add(new Point(5, 6));
points.add(new Point(6, 5));
points.add(new Point(10, 2));
points.add(new Point(10, 3));
points.add(new Point(11, 3));
Canopy canopy = new Canopy(points);
canopy.cluster();
//获取canopy数目
int clusterNumber = canopy.getClusterNumber();
System.out.println(clusterNumber);
//获取canopy中T2的值
System.out.println(canopy.getThreshold());
}
}
以上代码是对9个点使用Canopy算法进行计算,获取Canopy数目,也即K。
如有任何知识产权、版权问题或理论错误,还请指正。
转载请注明原作者及以上信息。